Targeting the Biology of Aging
Aging is the biggest modifiable risk factor for most chronic diseases and is caused by a discrete number of biological mechanisms that can be targeted therapeutically.

A New Approach
As we age, epigenetic markers called methyl groups accumulate on DNA and contribute to gene expression changes that may lead to disease. These epigenetic changes may result from lifestyle factors (e.g., smoking, drinking, etc.), aging, disease, and injury. Life Bio’s therapeutic approach targets the epigenetic alterations that contribute to multiple age-related diseases.
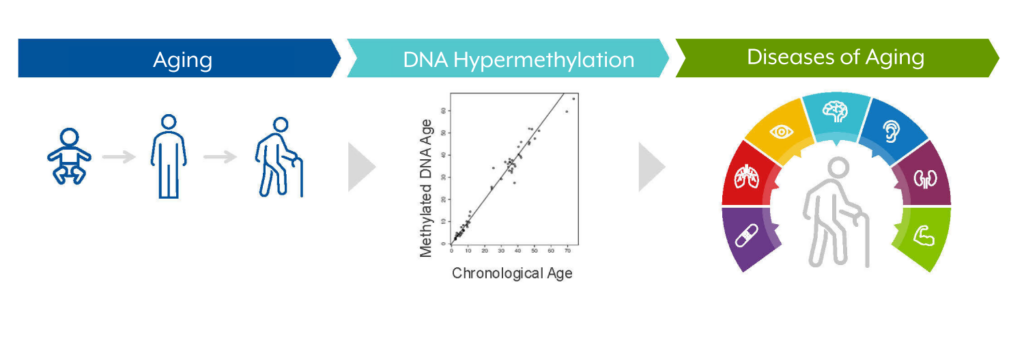
Our Focus
Life Bio’s therapies utilize three transcription factors – Oct-4, Sox-2, and Klf-4 (referred to as “OSK”) – that aim to reprogram the epigenome and thereby restore aged cells to a younger state, enabling more effective cell function.
Mechanism of Action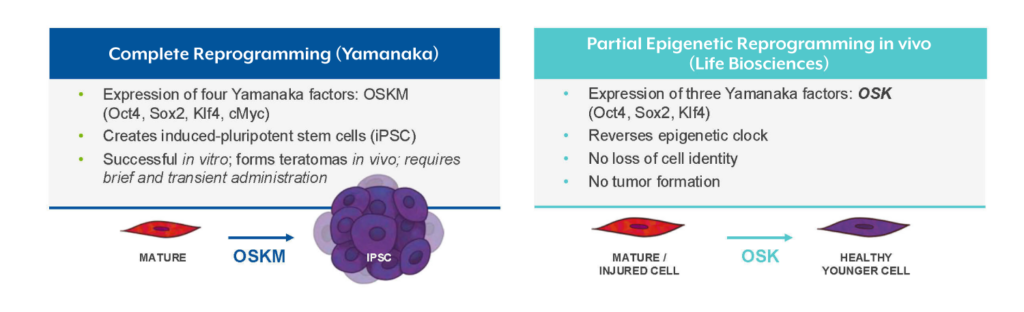
Life Bio’s lead gene therapy candidate, ER-100 (AAV2-OSK), has demonstrated safety and efficacy in multiple pre-clinical animal models by local injection into the eye (intravitreally). These data have been recognized as groundbreaking by multiple ophthalmology experts.
- ER-100 increased nerve regeneration following crush injury of the optic nerve in mice
- ER-100 restored vision in a mouse glaucoma model
- ER-100 significantly improved vision in naturally aged mice
- ER-100 restored visual function and increased nerve axon survival in a non-human primate (NHP) model of non-arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy (NAION)

